My young niece once asked me, “Is a dandelion a flower or a weed?”
Honestly, I was stumped. While I’m hardly a horticultural expert, I recognize that the dandelion has some attributes of a flower—including bright, colorful petals. But dandelions also behave like weeds, springing up all over our yards and stealing resources from our nice green lawns.
So I did what any smart uncle would do: I changed the subject and offered to buy her an ice cream.
Similarly, I think many B2B marketers would struggle to tell you whether their current sales tools are flowers or weeds. Are your sales tools truly helping to accelerate customers through the entire customer journey, or are they just springing up all over the place, with no proper order or control, and stealing resources from other communications efforts?
Weeding Out Ineffective Sales Tools
The reality is that some sales tools are flowers and some are weeds. If you’ve invested resources in sales tools that aren’t supporting your selling effort during at least one stage of the full, end-to-end customer journey, it may be time to weed out those ineffective sales tools. And if there are stages of that journey your tools aren’t properly supporting; you have more seeds to plant.
To ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of your marketing efforts, you need to ensure that you’re investing in the sales tools you need to accelerate the customer journey, without wasting effort on weak sales tools that only sap your resources. To do that, you’ll first need to map those tools to the various stages of the complete customer journey.
The Right Sales Tools for Each Stage
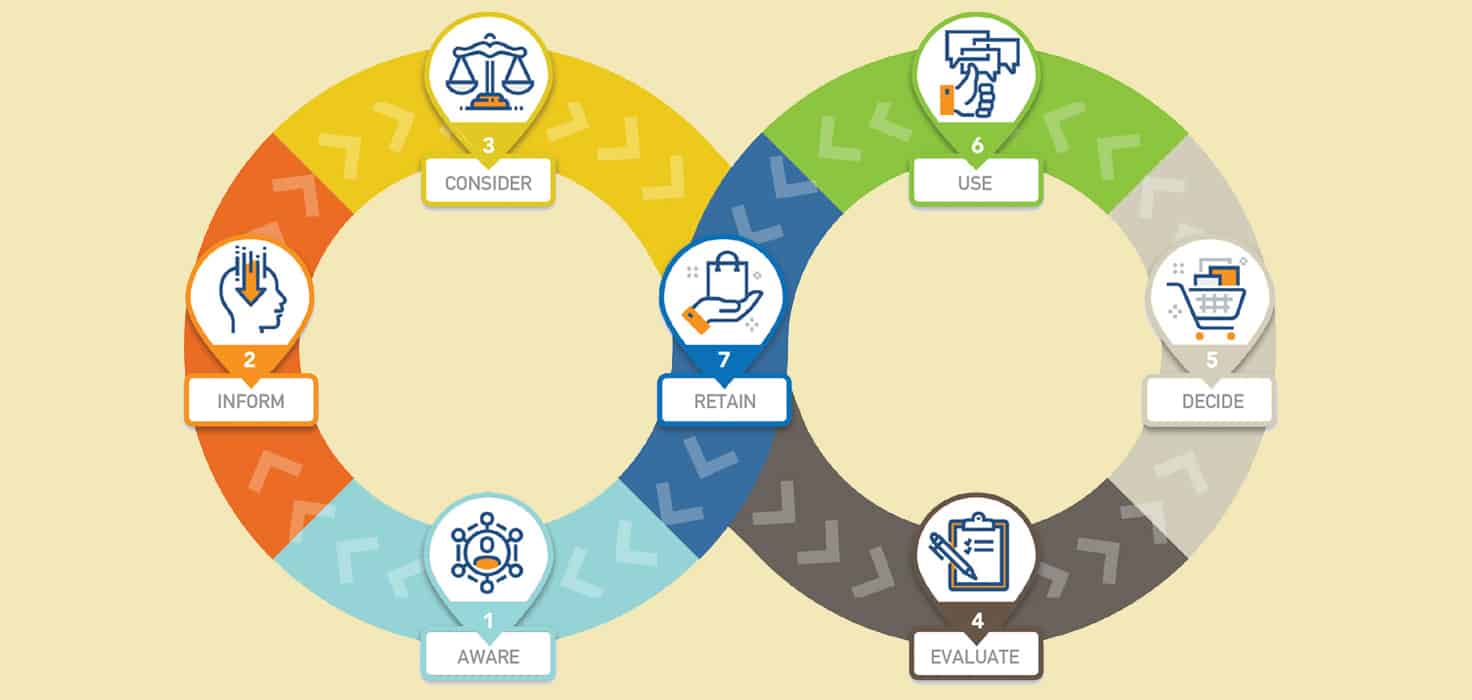
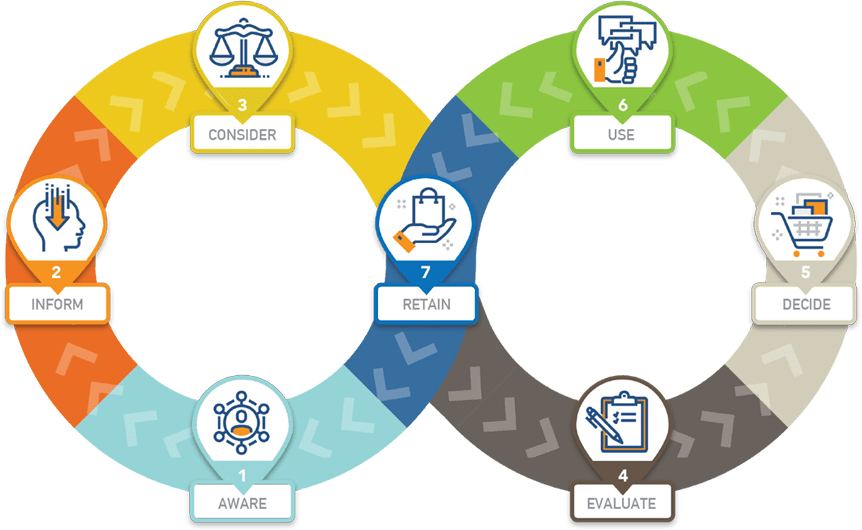
Let’s start by looking at the complete customer journey and each of its stages and discussing the typical role of sales tools at each stage.
1. Aware
At this earliest stage, sales tools should help the customer become aware of the problems, issues, and challenges that your product addresses. Such sales tools should help the customer evaluate their situation, identify the need, and understand that this is an issue that deserves further investigation because it can help overcome a significant challenge or accelerate a key business goal.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Content Marketing: High-quality, informative content like blog posts, articles, whitepapers, and case studies can help prospects understand the value of a product and recognize the challenges it addresses. This content can be shared through social media, email campaigns, and search engine optimization (SEO) efforts.
- Webinars and Workshops: Live or pre-recorded webinars and workshops are excellent tools for presenting the problem your product addresses and demonstrating how your solution can help. These interactive sessions allow prospects to ask questions and engage directly with experts, helping to build credibility and trust.
- Email Campaigns: Personalized email campaigns can help you target specific segments of your audience with tailored
- Social Media Marketing: Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, TikTok, Instagram and Twitter can be used to share valuable content and engage with prospects, and showcase your expertise.
2. Inform
At this stage, effective sales tools help inform customers who are generally aware of their overall need and will benefit from advice and guidance relevant to their specific environment and challenges. It is important to make customers aware that there are third-party products available to address their specific issues—without veering into any sales-oriented specifics.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Product Comparison Guides: These guides help prospects compare different solutions in the market, highlighting the features, advantages, and potential drawbacks of each. This allows customers to make an informed decision without feeling pressured by a sales pitch.
- Ebooks and Whitepapers: More in-depth than blog posts, ebooks and whitepapers offer detailed information on industry trends, best practices, and product-specific insights.
- Case Studies and Success Stories: Showcasing real-life examples of how your product has helped other customers can be persuasive in the inform stage. These stories provide tangible evidence of your product’s effectiveness in addressing specific challenges.
- Interactive Tools and Assessments: Offering tools like ROI calculators, needs assessments, or industry benchmarking tools can help prospects evaluate their current situation and identify areas where your product can provide value. These tools empower customers to make informed decisions based on their unique needs.
- Product Demos and Tutorials: In-depth product demos and tutorials can help prospects understand how your product works and how it can be applied to their specific challenges. These demos should focus on the functionality and benefits of your product without being overly sales-oriented.
3. Consider
At the consider stage of the customer journey, you will deploy sales tools that position your product as the ideal solution for addressing the business challenges and goals at hand. This is the stage for most traditional tools, such as company or product brochures.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Company/Product Brochures: These materials provide a comprehensive overview of your product’s features, benefits, and pricing. They should be visually appealing, easy to understand, and emphasize the unique value proposition of your product.
- Sales Presentations: A well-crafted sales presentation can effectively communicate your product’s value proposition, competitive advantages, and key differentiators. Tailor your presentation to address the specific needs and challenges of your prospect to demonstrate your understanding of their business.
- Free Trials: Allowing prospects to try your product can help them experience the benefits firsthand. This hands-on approach can be instrumental in converting prospects into customers.
4. Evaluate
In this stage, the customer clearly understands the issues and recognizes the need to pursue a solution. They are now looking for the product that best fits their needs based on their identified purchase criteria. At this stage, practical sales tools help convince the customer that your product is superior to the alternative choices (including third-party competitors and the status quo).
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- ROI and Cost-Benefit Analysis: Provide prospects with tools or case studies that demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) and cost savings associated with your product. This can help prospects see the tangible benefits of choosing your solution over alternatives.
- Tailored Demonstrations: Offer personalized demonstrations or proof-of-concept trials to show how your product can specifically address the prospect’s needs and challenges. This can be a powerful way to illustrate the effectiveness of your solution in their unique situation.
- Third-Party Validation: Share industry analyst reports, awards, or endorsements that showcase your product’s strengths and market position. This external validation can reinforce your product’s credibility and help persuade prospects of its superiority.
- Customer Testimonials and Reviews: Sharing positive experiences from satisfied customers can help build trust and credibility.
5. Decide
When it is time for customers to make their purchase decision, there are typically fewer but highly focused sales tools in use. The tools you use should help push the customer over the decision fence. They tend to focus on special offers and incentives that assist in that final push to closure.
While many marketers will focus on just the buyer’s journey—which ends with the purchase—it’s important to recognize that the full customer journey continues. You don’t stop communicating with people once they become customers; you adjust the nature of what, when, and how you communicate.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Money-Back Guarantees and Trial Periods: Providing prospects with the assurance that they can try your product risk-free can help eliminate any lingering doubts. Offering a money-back guarantee or trial period can instill confidence in your product and make the decision easier for the customer.
- Financing Options and Payment Plans: Offering flexible payment options can make your product more accessible and appealing to prospects. Providing financing options, payment plans, or deferred payment arrangements can help alleviate budgetary concerns and facilitate decision-making.
- Onboarding Support and Implementation Assistance: Reassuring prospects that they will receive dedicated support during the onboarding and implementation process can be a significant factor in their decision-making. Clear communication about the available resources and the expected timeline can help prospects feel confident in their choice.
6. Use
Communicating with new customers is vital to building strong customer relationships and loyalty. Sales tools developed for this stage of the customer journey typically focus on helping the customer get the maximum benefits from your product and recognize those benefits as a significant contributor to their total return on their investment.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Onboarding Guides and Tutorials: Providing step-by-step guides, video tutorials, and user manuals can help new customers get started with your product quickly and easily. These resources ensure a smooth onboarding process and promote a positive user experience.
- Knowledge Base and FAQs: An easily accessible knowledge base with answers to frequently asked questions can empower customers to troubleshoot issues and learn more about your product. This self-service resource can help reduce support requests and improve overall customer satisfaction.
- Training Programs and Workshops: Offering training sessions, workshops, or webinars can help customers learn how to use your product more effectively and efficiently. These educational resources can help customers maximize the benefits of your product and contribute to their success.
- Customer Support and Help Desk: Providing responsive and knowledgeable customer support is essential for resolving any issues that may arise during product use. A dedicated support team, live chat, or help desk can ensure customers receive timely assistance when needed.
- User Communities and Forums: Creating a space where customers can share their experiences, ask questions, and connect with other users can help foster a sense of community and encourage product engagement. This peer-to-peer support can also provide valuable insights for product improvements.
7. Retain
Once a customer has become a mature user of your products, the right sales tools can help encourage future purchases by promoting product upgrades, add-on products or other offerings. Sales tools are used to help keep customers loyal and engaged with your brand. Often such tools are designed to invite and encourage participation in customer loyalty programs, satisfaction surveys, customer forums, conferences, or workshops, or even to request testimonial statements or referrals.
Some examples of tools for this stage include:
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Implementing rewards and exclusive offers for loyal customers can incentivize repeat purchases and strengthen customer relationships. These programs can also help collect valuable data on customer preferences and behaviors.
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys and Feedback: Regularly soliciting customer feedback through surveys, reviews, or direct outreach can help identify areas for improvement and ensure customer satisfaction. This information can also guide product development and customer support initiatives.
- Newsletters and Product Updates: Keeping customers informed about new features, product updates, and company news can help maintain engagement and demonstrate your commitment to continuous improvement. Tailored content and personalized messages can also enhance the customer experience.
The Sales Tool Mapping Process
While the lists above do not include every possible sales tool, they do provide a solid sampling of the typical sales tools that are often used to support each stage of the customer journey. They can be used as a reference to help categorize and plan your sales tools and align them with the customer journey. Here are some recommended next steps and tips.
Audit your current sales tools.
First, you must audit your current sales tools and map them against the total customer journey. Create a grid that lists each tool under the seven stages of the customer journey. (Note that some tools can be mapped against multiple stages of the journey.)
As you fill in your own grid of current sales tools for each stage of the customer journey, you will begin to see where you have potential gaps—a lack of sales tools for a given stage. However, do not assume you need more tools for those stages. You won’t know that until you get through the next step.
Talk to your salespeople.
Find out where in the customer journey your sales team faces the most significant challenges. Is it getting customers’ attention and making them aware of the problems your products address? Then perhaps you need to examine the quantity and effectiveness of the sales tools you’ve mapped to the aware stage. Or perhaps the real issue is dealing with specific competitive challenges, and you need more effective sales tools for the evaluate stage.
The areas where you need to improve your tools are not necessarily those where you have the fewest. For example, even if you lack sales tools for the inform stage, there’s no point in creating more if your sales team tells you they don’t have any challenges finding educated, informed prospects. Perhaps the real problem is that prospects in the consideration stage just don’t perceive your solution as a top contender. Or perhaps the sales organization keeps losing to competitors in the evaluation stage.
The bottom line is that you need to find out where your sales opportunities are most often being slowed or thwarted—and then focus on creating sales tools that align with those opportunities to accelerate the total customer journey. And that all starts with talking to your salespeople.
Create a content marketing strategy.
While today’s B2B marketers say they are committed to developing a content marketing strategy for their company, many have not actually documented that strategy. Without a documented strategy, the development of sales tools is often reactionary. You develop sales tools in response to specific activities (e.g., new product launches, upcoming trade shows or conferences, threatening competitive product releases, new sales promotions, or upcoming email campaigns). This can result in a haphazard collection of tools that don’t help to accelerate prospects through the complete customer journey.
A content marketing strategy helps to ensure that you are creating sales assets that drive profitable customer action. A good content marketing strategy will also help you set priorities; this is important because few marketing organizations have the resources or expertise to develop all the content they need.
Don’t ignore the early stages of the customer journey; they still matter.
With the shift in customer savviness fueled by fingertip access to volumes of research, reports and information, it’s easy for B2B marketers to conclude that today’s buyers don’t want to hear from vendors until late in the customer journey. Assuming this is the case, many companies have refocused their selling efforts on the middle stages of the journey. But this could well be a mistake.
In many cases, it’s not that buyers don’t want to hear from you in their early investigative efforts. They don’t want to be presented with sales pitches or product details. They’re still interested in gaining information and insights into their challenges. If you can add real value to their efforts to gain knowledge and insights, B2B buyers are open to hearing from you.
Don’t forget the status quo.
It’s common for B2B marketers—especially technology companies—to focus sharply on competitors. But here’s an important fact: You will likely lose more business to the decision to do nothing than to all other competitors combined.
So, when planning sales tools for the consider and evaluate stages, consider messages focused on helping risk-averse buyers realize that doing nothing is a greater and potentially more costly risk than moving forward with your solution.
Get Smarter and More Effective
It’s not difficult to waste resources creating sales tools that offer only modest, if any, return on your investment. And it’s all too easy to overlook even the simplest tools that can most effectively drive customers to your desired outcome. By understanding your total customer journey and mapping your sales tools to it, you gain perspective and insights that will help bring more strategy to your marketing efforts—and ultimately result in smarter and more effective sales-tool investments.
Empower Your Product Strategy with the Pragmatic Institute Foundations Course
Are you ready to take your product strategy to new heights? Join the Pragmatic Institute Foundations course and learn how to:
✓ Gain a deep understanding of the market and its challenges
✓ Leverage market insights to create in-demand products
✓ Master the Pragmatic Framework for successful product development
✓ Listen to the market, prioritize projects, and drive impactful results
Equip yourself with the skills and knowledge to excel as a market-driven product professional. Don’t let this opportunity pass you by – seize the chance to transform your career today.
Author
-

Rod Griffith, a seasoned professional with 41 years in product marketing, has left an indelible mark at Control Module Inc., Data General, Cultural Organization of Lowell, and MarketReach, Inc. His expertise spans strategic marketing, brand development, channels marketing, and strategic alliances. Rod excels in crafting effective integrated marketing programs for technology, business, and healthcare solutions. For questions or inquiries, please contact [email protected].
View all posts