4-minute read
This article explores the essential communication skills that every data analyst should master.
The ability to analyze and interpret complex business data has become more important than ever. Yet, beyond the numbers and algorithms lies a skill equally critical but less discussed: communication. As the demand for data analysts increases, those who can effectively convey their findings to diverse audiences not only have an advantage in the job market but can also shape the future of business with data-driven decision-making.
Ready to learn five effective communication skills for data analysts? Keep reading, or use the links below to jump to the section that most interests you:
- Importance of communication skills for data analysts
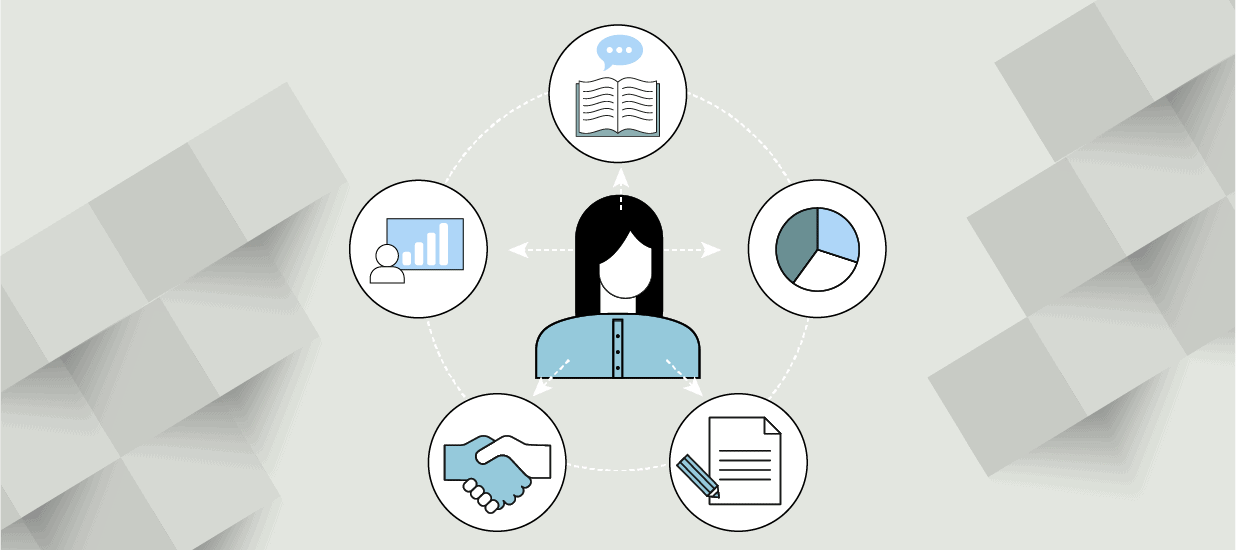
- Skill #1: Data Storytelling
- Skill #2: Data Visualization
- Skill #3: Written Communication
- Skill #4: Interpersonal Skills
- Skill #5: Presentation Skills
Why is it important for data analysts to have strong communication skills?
Data analysts need technical and mathematical skills to gather, analyze, and interpret complex data from various sources. However, communication skills are also essential for successful data analysts. That’s because data analysts need to be able to explain their analyses, data models, and findings to teammates, clients, and executive stakeholders. It is also essential that data analysts share justifications for their conclusions and their implications for businesses. Logistically, clear communication helps teams align on project goals, timelines, and deliverables.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts demand for data analysts will grow by 35% between 2022 and 2032. As demand for this competitive role grows, data analysts need strong communication skills to stay competitive in the job market and effective in their jobs. Investing in your communication skills is not just nice to have; it’s necessary for your career growth and job security.
Skill #1: Data Storytelling
With endless dashboards, spreadsheets, and charts, data analysts can engage stakeholders with compelling storytelling that thoroughly explains the findings. Data storytelling involves mapping data and numbers against a narrative to help improve data comprehension and create investment in the findings. Rather than requiring your audience to parse through complex numbers, it helps them focus on the key insights. It removes all the noise and focuses on the key insights.
Why is it important? Data storytelling is an essential skill for data analysts because it helps engage stakeholders, simplify complex information, and help teams make data-based, strategic decisions.
Example: When presenting sales data, a data analyst might show that sales decreased period-over-period. Instead of simply showing the trend, a savvy communicator will dig into the data to understand the cause of a downturn and create suspense as they share what generated it. Then, they can follow a data storytelling narrative arc to share discoveries and bring the audience to a resolution by providing data-based recommendations.
How can data analysts learn data storytelling? It’s not as daunting as it may seem. By studying data storytelling frameworks and practicing linking data insights with strategic business outcomes, you can take your audience on a hero’s journey. This practical approach will give you the confidence to effectively communicate complex data in a compelling way.
Skill #2: Data Visualization
As human brains process visuals 60,000 times faster than text, data visualization is a critical skill for data analysts. Data visualization helps individuals interpret the data visually, allowing them to absorb the insights and drive business decisions quickly. Data visualization uses graphics like line graphs, area charts, tables, pie charts, and numeric scorecards. Additionally, robust data visualizations call attention to critical insights, such as by offsetting important information in different colors or using data callouts.
Why is it important? Visualizations help communicators share the most important insights from their data. Data visualization also aids comprehension among audiences by highlighting key information and the same data elements for everyone in the audience.
Example: When you need to share insights about a specific market segment, a talented data analyst might tailor a presentation to set data for that market segment apart visually from other market segments using different colors.
How can data analysts learn data visualization? Data analysts should complete data visualization courses to learn best practices for data literacy and visual communication. Practice creating your visualizations using Excel, Google’s Looker Studio, Microsoft PowerBI, or Tableau. Then, share your visualizations with colleagues and ask for feedback.
Skill #3: Written Communication
Writing precisely and concisely is essential for data analysts. Analysts might summarize findings in presentations, report documents, or even emails. Strong written communication skills help you adapt your message to any audience and make it appropriate to the channel through which you are communicating.
Why is it important? Strong written communication skills help you tailor your communication to ensure your findings are understood and actionable. Taking the time to write clearly and concisely can prevent confusion or misinterpretation of the data.
Example: A data analyst can report on the results of a marketing campaign by clearly summarizing the context behind the data, how it was collected and analyzed, and highlighting key findings. By using clear written communication, marketing team members can understand the campaign’s results and adapt their strategies based on data.
How can data analysts improve their written communication skills? Take online courses on business writing to learn the best practices you can implement in your job. Practice regularly and ask for feedback from colleagues and mentors to help you improve.
Skill #4: Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills encompass the ability to interact effectively with colleagues and stakeholders. They help you relate to others through empathy, form lasting connections, negotiate to reach common agreements, and resolve conflict. Essentially, these are the skills that make you “good with people.”
Why is it important? Interpersonal skills in the workplace help form a collaborative environment that upholds psychological safety and helps teams work through obstacles to achieve common goals. For data analysts, this helps navigate the complexities of business needs (and sometimes conflicting priorities) and improves collaboration.
Example: Data analysts use interpersonal skills to facilitate conversations between departments and identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that effectively measure the performance of individual teams and the company.
How can data analysts improve their interpersonal skills? Participate in team-building activities and leverage free resources like webinars and podcasts to improve these skills on your own time. You can also build empathy by working to consider others’ perspectives, asking for input, and requesting feedback during difficult conversations.
Skill #5: Presentation Skills
Strong presentation skills combine the essential elements of data visualization, storytelling, and written and interpersonal communication skills. It involves presenting data and insights using visualization tools or presentation decks to share important information and ensure comprehension from your audience. Knowing how to tailor your information to fit your audience’s needs and skill levels and compellingly delivering that tailored information is an essential skill for data analysts. Beyond merely presenting the data, speaking clearly and concisely, making eye contact with your audience, and leveraging your body language to communicate key points can bolster your presentation.
Why is it important? Data analysts might give presentations to audiences of all skill levels. The goal is to present data without confusing, overwhelming, or intimidating the audience. Not only presenting the information but also presenting it in a way that helps your audience understand it and feel invested in it is a powerful skill for any employee.
Example: A data analyst may give quarterly presentations on product quality and revenue to executive stakeholders.
How can data analysts improve their presentation skills? Practice, practice, practice! Ask for opportunities to present data to colleagues (even when it’s not required). Get feedback on your presentation skills and ask for advice from presenters you admire.
Author
-

The Pragmatic Editorial Team comprises a diverse team of writers, researchers, and subject matter experts. We are trained to share Pragmatic Institute’s insights and useful information to guide product, data, and design professionals on their career development journeys. Pragmatic Institute is the global leader in Product, Data, and Design training and certification programs for working professionals. Since 1993, we’ve issued over 250,000 product management and product marketing certifications to professionals at companies around the globe. For questions or inquiries, please contact [email protected].
View all posts